- Space
- Astronomy
Astronomers have revealed a new type of cosmic object called Cloud-9 — a dim, starless gas cloud anchored by a massive dark matter halo that may be the first-confirmed failed galaxy.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.
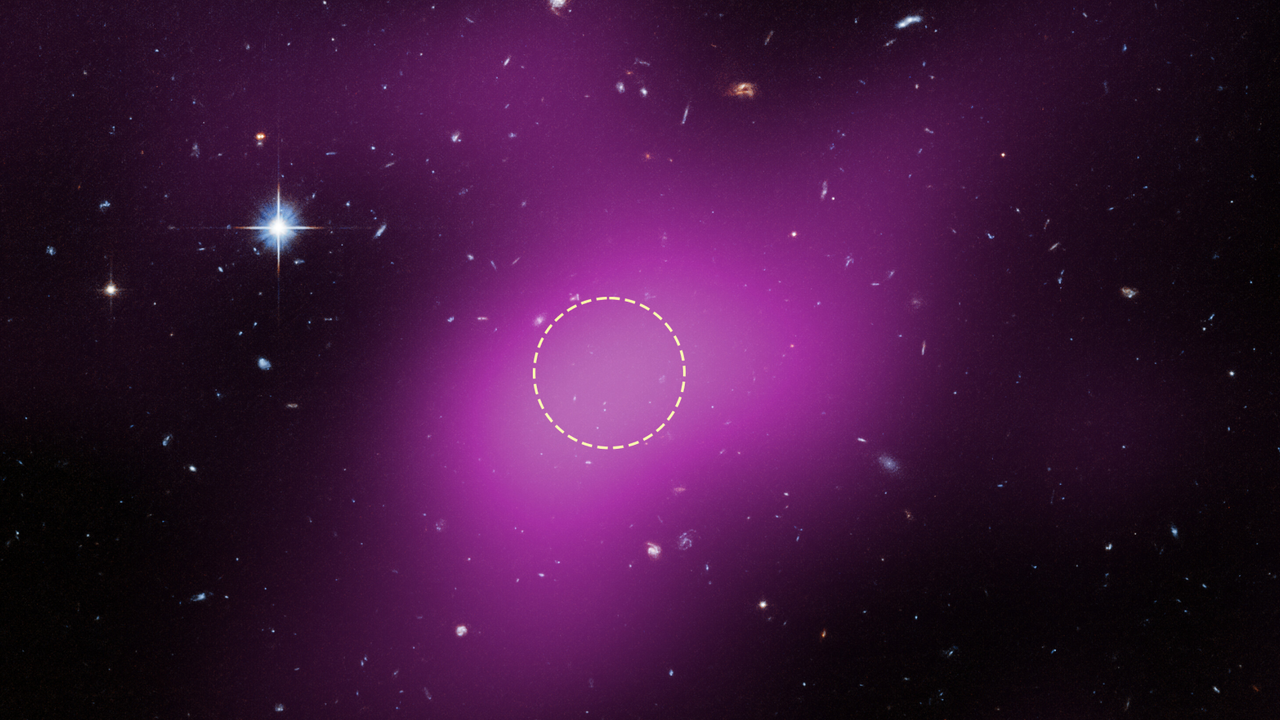
 At the center of the dashed circle hides Cloud-9 — a rare type of ‘failed galaxy’ loaded with hydrogen and dark matter, but no discernible stars.
(Image credit: NASA, ESA. G. Anand (STScI), and A. Benitez-Llambay (Univ. of Milan-Bicocca); Image processing: J. DePasquale (STScI))
Share
Share by:
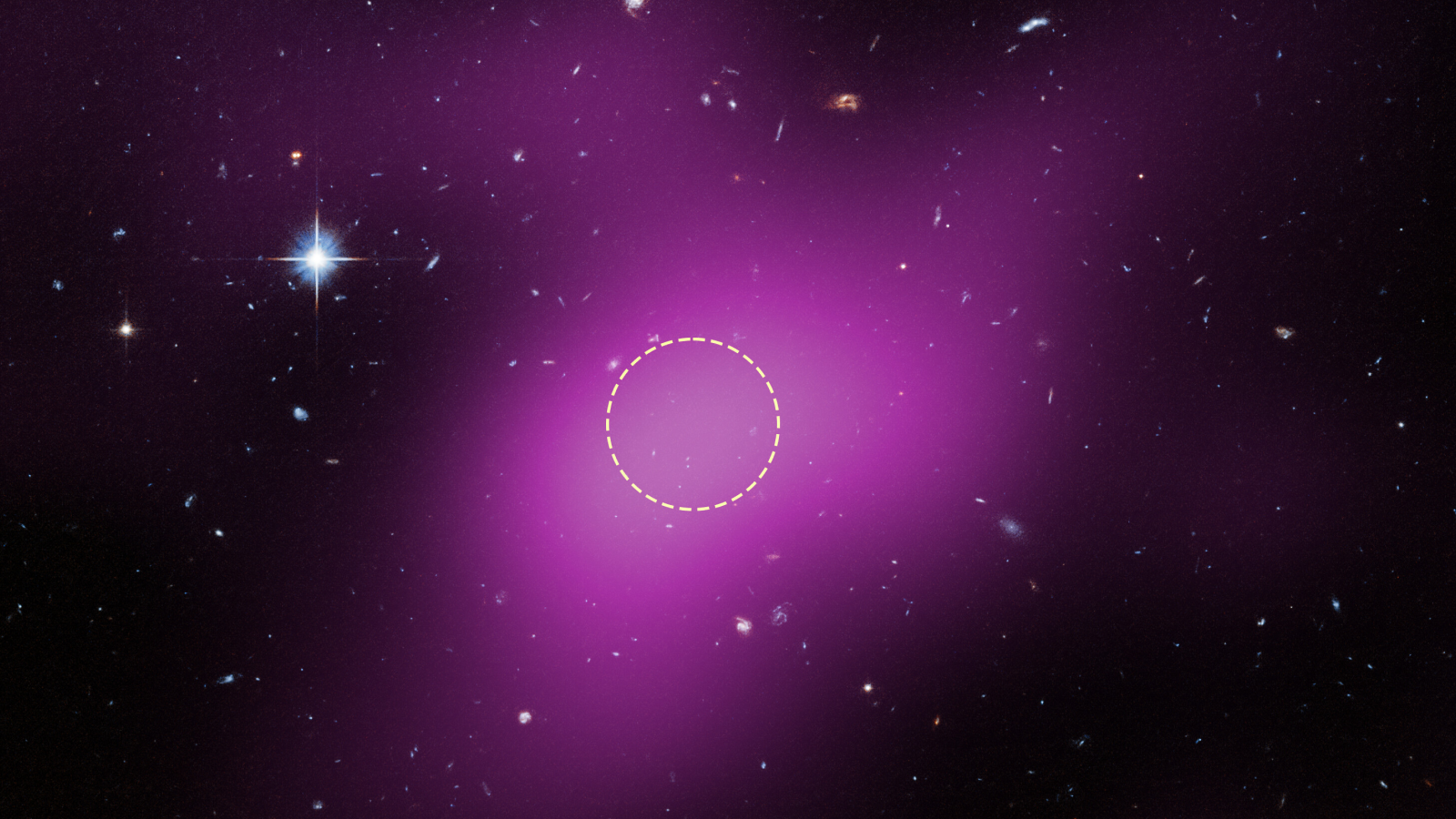
At the center of the dashed circle hides Cloud-9 — a rare type of ‘failed galaxy’ loaded with hydrogen and dark matter, but no discernible stars.
(Image credit: NASA, ESA. G. Anand (STScI), and A. Benitez-Llambay (Univ. of Milan-Bicocca); Image processing: J. DePasquale (STScI))
Share
Share by:
- Copy link
- X
Astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope have just spotted a new type of celestial object: Cloud-9, a starless, gas-rich cloud of dark matter that was slightly too light to become a full-fledged galaxy.
As detailed in a study published Nov. 10 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters and presented this week at the 247th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Phoenix, this odd object is located more than 14 million light-years from Earth, near the spiral galaxy Messier 94 (M94). Cloud-9 is a cosmic relic, a primordial building block of galaxies that confirms the critical mass threshold needed for a body of gas and dark matter to collapse into a galaxy.
As a result, the discovery of Cloud-9 strongly supports a cornerstone of the leading cosmological framework that aims to explain the structure and composition of the universe — the Lambda cold dark matter model (LCDM). One of the model's major predictions is that dark matter settles in halos, which may or may not grow heavy enough to anchor galaxies.
You may like-
 Record-breaking 'dark object' found hiding within a warped 'Einstein ring' 10 billion light-years away
Record-breaking 'dark object' found hiding within a warped 'Einstein ring' 10 billion light-years away
-
 Did a NASA telescope really 'see' dark matter? Strange gamma-rays spark bold claims, but scientists urge caution
Did a NASA telescope really 'see' dark matter? Strange gamma-rays spark bold claims, but scientists urge caution
-
 'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
"These 'dark halos' should be plentiful, however most of them do not retain any hydrogen gas, thus remaining invisible," Deep Anand, astronomer at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) and the study's lead author, told Live Science via email. "Cloud-9 lies at the very upper end of the dark halo mass range, thus allowing it to retain its gas, and therefore being visible through radio observations. This is indeed a strong confirmation of a cornerstone prediction of LCDM."
Accordingly, Cloud-9 offers the first hint of evidence that the universe could be teeming with low-mass dark matter halos that remain devoid of stars, as theory predicts.
Digging up a cosmic fossil
Astronomers discovered Cloud-9 three years ago with the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) in Guizhou, China. The massive radio telescope has been "very productive in finding similar clouds" and may find others in the future, study co-author Andrew Fox, also an astronomer at STScI, told Live Science via email.
Previously, the researchers used the Very Large Array, a 28-telescope array in New Mexico, to focus on the peak of Cloud-9's radio emissions, originating from its 5,000-light-year wide core. However, the observations failed to identify the object's true nature, potentially owing to telescope sensitivity limits. Perhaps Cloud-9 was simply a ho-hum dwarf galaxy that was too faint to be properly viewed by ground-based facilities, the researchers considered.
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter nowContact me with news and offers from other Future brandsReceive email from us on behalf of our trusted partners or sponsorsBy submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.But, as described in the new study, a follow-up with the Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys revealed a much rarer phenomenon, one that astronomers had been seeking for years: a "theoretical phantom object" and the first-ever confirmed RELHIC, or Reionization-Limited H I Cloud. In other words, a cloud of neutral hydrogen, a natal leftover from the early cosmos and a unique "window into the dark universe," Fox said in a NASA press statement.
This hydrogen detection was proof that Cloud-9 was not a typical dwarf galaxy, but something stranger.

To be or not to be a galaxy
The researchers analyzed the gas in Cloud-9 based on the radio waves it emits, and found the gas contributes about one million suns worth of mass to the strange object. That alone is not enough to keep such a large gas cloud together. So, assuming that the system is held together by a balance between gravity, gas pressure, and gas heating, Cloud-9's dark matter component must weigh in at around five billion solar masses, the team calculated.
You may like-
 Record-breaking 'dark object' found hiding within a warped 'Einstein ring' 10 billion light-years away
Record-breaking 'dark object' found hiding within a warped 'Einstein ring' 10 billion light-years away
-
 Did a NASA telescope really 'see' dark matter? Strange gamma-rays spark bold claims, but scientists urge caution
Did a NASA telescope really 'see' dark matter? Strange gamma-rays spark bold claims, but scientists urge caution
-
 'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
This mass hits a sweet spot "remarkably close" to the independently theorized critical mass threshold. At this threshold, Cloud-9 falls just short of having enough mass to collapse into a galaxy, but is massive enough, due to its dark matter component, to keep itself together.
Cloud-9 is also in thermal equilibrium with the cosmic ultraviolet (UV) background, the UV energy streaming from all the universe's stars, active black holes, and hot gas. This energy keeps gas ionized, or electrically charged, and relatively hot, suppressing galaxy formation. This also contributes to the cloud's total lack of stars.
However, the researchers conclude that Cloud-9 may not be irrevocably doomed to eternal darkness. It may still gather enough mass to become a galaxy, though the exact mechanics that would allow this are speculative.
Whatever its fate, Cloud-9 serves as a physical benchmark that shows that current dark matter models, as well as galaxy formation theories, are on the right track.
An exceedingly rare relic from the ancient universe
Future studies will search for failed galaxies similar to Cloud-9 — though finding them is much easier said than done, for multiple reasons. First, such dim objects are easily outshined by other celestial sources.
These clouds are also ephemeral, and likely to be eradicated by a process known as ram pressure stripping, which robs them of their gas as they move through intergalactic space. In fact, Cloud-9 appears to be already perturbed by the relatively hot circumgalactic medium around its neighbor galaxy, M94, the researchers said.
RELATED STORIES—Vera C. Rubin Observatory discovers enormous, record-breaking asteroid in first 7 nights of observations
—'How can all of this be happening?': Scientists spot massive group of ancient galaxies so hot they shouldn't exist
—Hidden 'doomed' star revealed by James Webb Space Telescope could solve decades-old mystery
"To survive as a dark, gas-rich cloud into the present-day, a system must meet two stringent, and statistically rare, criteria," Alejandro Benitez-Llambay, principal investigator of the program to study Cloud-9 and an astrophysicist at the University of Milano-Bicocca, told Live Science via email. "First, its dark matter halo must have an atypically slow assembly history; if it grew too quickly in the early universe, the gas would have collapsed to form stars before the cosmic UV background could heat it up. Second, the system must remain sufficiently isolated." Fewer than 10% of such gas clouds may have remained as starlessly pristine as Cloud-9, Benitez-Llambay added.
Finally, as a dark-universe ambassador, Cloud-9 is a crucial reminder that the stunning panoramas of stars we see in most astronomical images represent a small proportion of the cosmos as a whole — the shiny things we can see tell only part of the cosmological story.
Ivan FarkasLive Science ContributorIvan is a long-time writer who loves learning about technology, history, culture, and just about every major “ology” from “anthro” to “zoo.” Ivan also dabbles in internet comedy, marketing materials, and industry insight articles. An exercise science major, when Ivan isn’t staring at a book or screen he’s probably out in nature or lifting progressively heftier things off the ground. Ivan was born in sunny Romania and now resides in even-sunnier California.
Show More CommentsYou must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.
Logout Read more Record-breaking 'dark object' found hiding within a warped 'Einstein ring' 10 billion light-years away
Record-breaking 'dark object' found hiding within a warped 'Einstein ring' 10 billion light-years away
 Did a NASA telescope really 'see' dark matter? Strange gamma-rays spark bold claims, but scientists urge caution
Did a NASA telescope really 'see' dark matter? Strange gamma-rays spark bold claims, but scientists urge caution
 'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
'Puzzling' object discovered by James Webb telescope may be the earliest known galaxy in the universe
 Astronomers close in on signal from Epoch of Reionization
Astronomers close in on signal from Epoch of Reionization
 Astronomers spot giant hidden 'bridge' and record-breaking tail between 2 dwarf galaxies
Astronomers spot giant hidden 'bridge' and record-breaking tail between 2 dwarf galaxies
 Mysterious galaxy trapped in 'the void' keeps churning out stars without fuel
Latest in Astronomy
Mysterious galaxy trapped in 'the void' keeps churning out stars without fuel
Latest in Astronomy
 James Webb telescope confirms a supermassive black hole running away from its host galaxy at 2 million mph, researchers say
James Webb telescope confirms a supermassive black hole running away from its host galaxy at 2 million mph, researchers say
 Vera C. Rubin Observatory discovers enormous, record-breaking asteroid in first 7 nights of observations
Vera C. Rubin Observatory discovers enormous, record-breaking asteroid in first 7 nights of observations
 NASA telescope combines 100 maps of the universe into one, promising huge discoveries
NASA telescope combines 100 maps of the universe into one, promising huge discoveries
 'How can all of this be happening?': Scientists spot massive group of ancient galaxies so hot they shouldn't exist
'How can all of this be happening?': Scientists spot massive group of ancient galaxies so hot they shouldn't exist
 The moon has been secretly feasting on Earth's atmosphere for billions of years
The moon has been secretly feasting on Earth's atmosphere for billions of years
 'Wolf Supermoon' gallery: See the first full moon of 2026 in pictures from across the world
Latest in News
'Wolf Supermoon' gallery: See the first full moon of 2026 in pictures from across the world
Latest in News
 NASA cancels spacewalk and considers early crew return from ISS due to medical issues
NASA cancels spacewalk and considers early crew return from ISS due to medical issues
 Hubble telescope discovers 'Cloud-9,' a dark and rare 'failed galaxy' that's unlike anything seen before
Hubble telescope discovers 'Cloud-9,' a dark and rare 'failed galaxy' that's unlike anything seen before
 Orbiting satellites could start crashing into one another in less than 3 days, theoretical new 'CRASH Clock' reveals
Orbiting satellites could start crashing into one another in less than 3 days, theoretical new 'CRASH Clock' reveals
 New US food pyramid recommends very high protein diet, beef tallow as healthy fat option, and full-fat dairy
New US food pyramid recommends very high protein diet, beef tallow as healthy fat option, and full-fat dairy
 Rare 2,000-year-old war trumpet, possibly linked to Celtic queen Boudica, discovered in England
Rare 2,000-year-old war trumpet, possibly linked to Celtic queen Boudica, discovered in England
 Leonardo da Vinci's DNA may be embedded in his art — and scientists think they've managed to extract some
LATEST ARTICLES
Leonardo da Vinci's DNA may be embedded in his art — and scientists think they've managed to extract some
LATEST ARTICLES 1Hubble telescope discovers 'Cloud-9', a dark and rare 'failed galaxy' that's unlike anything seen before
1Hubble telescope discovers 'Cloud-9', a dark and rare 'failed galaxy' that's unlike anything seen before- 2NASA cancels spacewalk and considers early crew return from ISS due to medical issues
- 3James Webb telescope confirms a supermassive black hole running away from its host galaxy at 2 million mph, researchers say
- 4Orbiting satellites could start crashing into one another in less than 3 days, theoretical new 'CRASH Clock' reveals
- 5Vera C. Rubin Observatory discovers enormous, record-breaking asteroid in first 7 nights of observations